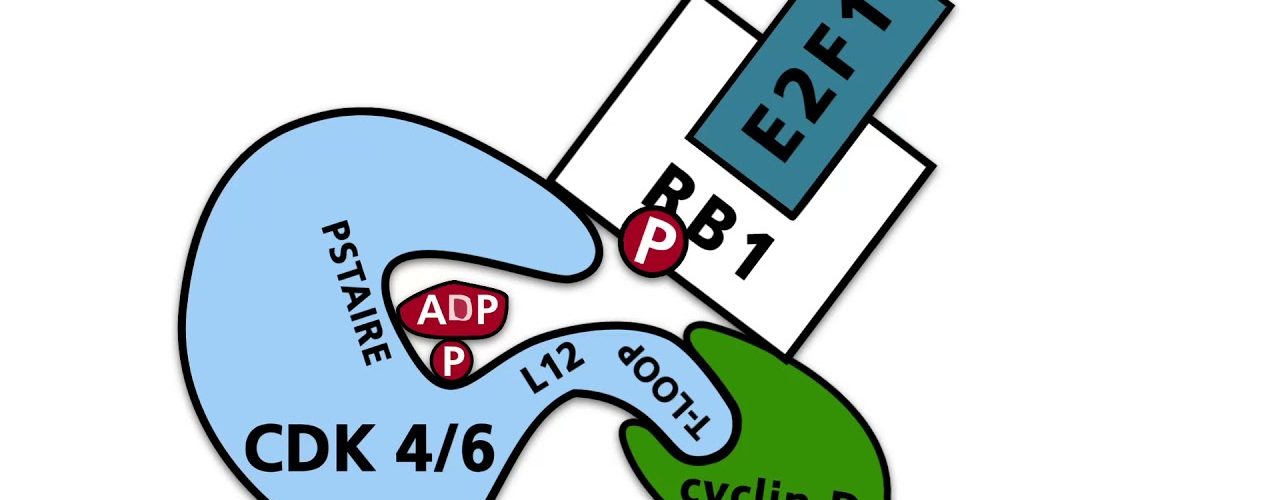
The most important family of receptor tyrosine kinases is the family of the receptors for EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor). Activation of the EGF...
Category - Onkoview 2015
The EGF receptor tyrosine protein kinases and the therapy of tumors with activated EGF receptors – Part 1: Inhibition of receptor activation via antibodies
In many tumors, EGF receptors are over-activated, which leads to a stronger signal and a high rate of proliferation. In order to inhibit the signal...
The EGF receptor tyrosine protein kinases and the therapy of tumors with activated EGF receptors – Part 2: Blocking of EGF receptor signaling via tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Tumors with activated EGF receptors can be treated with drugs that inhibit the kinase activity by binding to intracellular domains. Most of these...
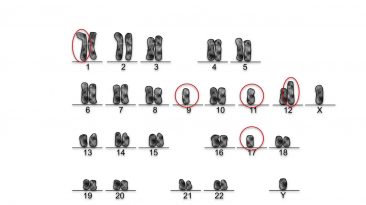
More than 50 years ago, researchers detected typical chromosomal abnormalities in blood cells of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). These...
The Philadelphia chromosome, which is found in leukemic cells in more than 90% of all patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), results from a...
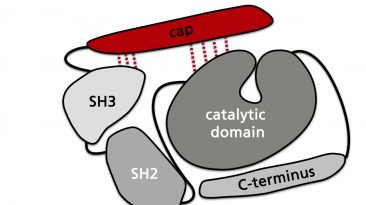
The gene product of the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene is a kinase with a higher activity compared to the activity of the native ABL1 kinase. The analysis of...
BCR-ABL1 and the Philadelphia chromosome – Part 4: Therapy of tumors with BCR-ABL1 fusion proteins
The specific BCR-ABL1 inhibitor molecule Glivec was the first anti-cancer drug to be developed against a tumor-specific protein. Glivec binds to the...
In tumor cells of patients with congenital hamartoma syndromes such as Cowden syndrome (CS), tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) syndrome and Peutz...
The TGF-beta superfamily comprises several different extracellular factors. The factors bind to and activate the membrane-bound TGF-beta receptor...
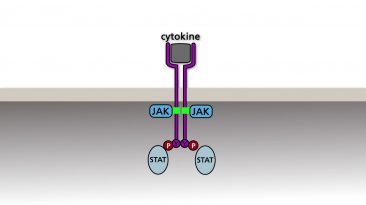
The JAK/STAT pathway begins with the activation of a membrane bound cytokine receptor by interferon or another cytokine. The activated receptor...