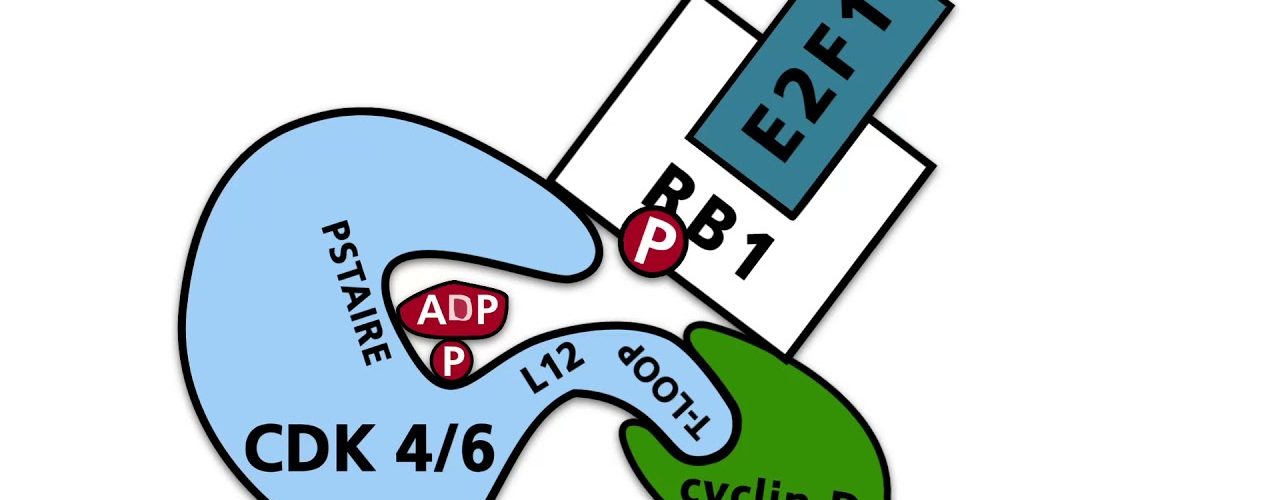
In normal cells, activation of the hedgehog signaling pathway begins with the binding of the extracellular hedgehog protein to the membrane receptor...
Category - Onkoview 2015
The hedgehog signaling pathway – Part 2: Activation of the Hedgehog pathway in basal cell carcinoma and medulloblastoma
The hedgehog signaling pathway is constitutively active in cells of basal cell carcinoma and medulloblastoma. This activation is caused by the...
The hedgehog signaling pathway – Part 3: Inhibition of the Hedgehog pathway by drugs binding to Smoothened
Tumor cells with constitutively active hedgehog signaling pathway can be treated with drugs that bind directly to and inhibit Smoothened...
The notch receptor consists of an extracellular domain that is non-covalently linked to a protein with a transmembrane and an intracellular domain...
NF-κB transcription factors can be activated by different pathways. The canonical NF-κB pathway starts with the activation of the TNFα receptor. The...
The alternative NF-κB pathway is activated by several ligands such as CD40L or lymphotoxin β and their receptors. The activated receptor lifts the...
The NF-kB pathway is constitutively active in multiple myeloma and other human tumors. The activation is based mainly on mechanisms that lead to...
Cells within growing tissues need a constant supply of oxygen. Under physiological conditions, the delivery of oxygen is well regulated; under...
Hypoxia Inducible Factors (HIFs), Part 2: Regulation of HIF under normoxic and hypoxic conditions
The Hypoxia Inducible Factor (HIF) is a transcription factor, which consists of an a and a β subunit. One of three α subunits dimerizes...
The SCLC2A1 gene, which encodes a type 1 glucose transporter (GLUT1), responds to both HIF1α and HIF2α. Thus, both factors increase the...