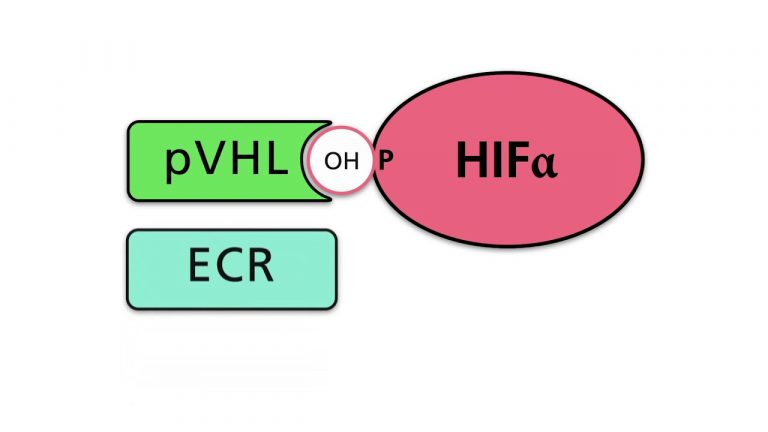
The Hypoxia Inducible Factor (HIF) is a transcription factor, which consists of an a and a β subunit. One of three α subunits dimerizes with one of two β subunits. The α subunits are sensitive to oxygen, whereas the β subunits are not. In this video, the domain structure...
Latest videos
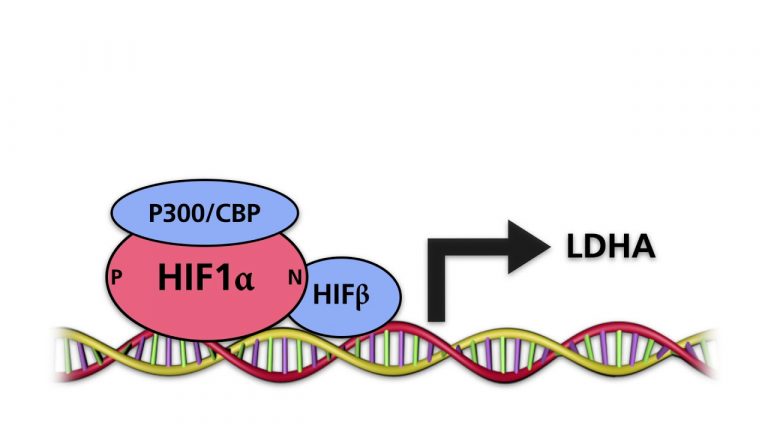
The SCLC2A1 gene, which encodes a type 1 glucose transporter (GLUT1), responds to both HIF1α and HIF2α. Thus, both factors increase the cellular uptake of glucose. HIF1α activates the transcription of genes encoding enzymes involved in glycolysis. HIF1α stimulates the synthesis...
The general principles of signal transduction can by compared to air traffic between different countries, where countries symbolize the cells and airplanes carrying passengers or cargo symbolize the signal-transmitting proteins. These proteins bind to membrane-anchored receptors, which...
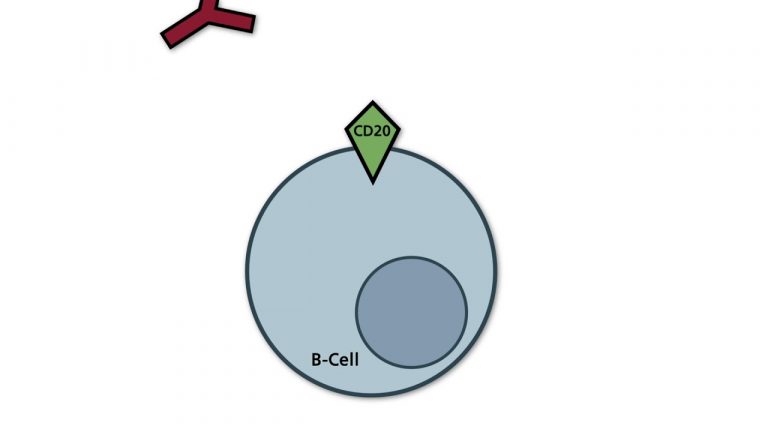
In the context of cancer therapy, antibodies produced outside the patient are used which are directed against secreted factors, membrane receptors or surface antigens of tumor cells. In order to avoid an immune reaction against the foreign protein in the patient, the domains outside the...
Effects of proteinases with metalloproteinase domains (MMPs, ADAMs) on tumour progression
By degradation of cell adhesion molecules, metalloproteases increase the motility of epithelial cells. Growth factors, which are bound to the plasma membrane, are released. In this way, the growth factors can reach their receptors on target cells. Growth factors, for example TGF-b, may...