The TGF-beta superfamily comprises several different extracellular factors. The factors bind to and activate the membrane-bound TGF-beta receptor, which is a serine...
Video
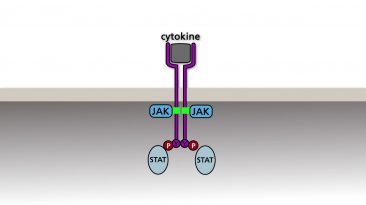
The JAK/STAT pathway begins with the activation of a membrane bound cytokine receptor by interferon or another cytokine. The activated receptor recruits and activates...
In normal cells, activation of the hedgehog signaling pathway begins with the binding of the extracellular hedgehog protein to the membrane receptor Patched. The...
The hedgehog signaling pathway – Part 2: Activation of the Hedgehog pathway in basal cell carcinoma and medulloblastoma
The hedgehog signaling pathway is constitutively active in cells of basal cell carcinoma and medulloblastoma. This activation is caused by the mutational inactivation or...
The notch receptor consists of an extracellular domain that is non-covalently linked to a protein with a transmembrane and an intracellular domain. Notch signaling is...
NF-κB transcription factors can be activated by different pathways. The canonical NF-κB pathway starts with the activation of the TNFα receptor. The activated receptor...
The alternative NF-κB pathway is activated by several ligands such as CD40L or lymphotoxin β and their receptors. The activated receptor lifts the blockage of the...
The NF-kB pathway is constitutively active in multiple myeloma and other human tumors. The activation is based mainly on mechanisms that lead to an increased level...
Cells within growing tissues need a constant supply of oxygen. Under physiological conditions, the delivery of oxygen is well regulated; under pathological conditions...
Hypoxia Inducible Factors (HIFs), Part 2: Regulation of HIF under normoxic and hypoxic conditions
The Hypoxia Inducible Factor (HIF) is a transcription factor, which consists of an a and a β subunit. One of three α subunits dimerizes with one of two β...