The notch receptor consists of an extracellular domain that is non-covalently linked to a protein with a transmembrane and an intracellular domain. Notch signaling is initiated by the binding of a membrane-bound ligand to the extracellular domain of the Notch receptor of a neighboring...
Layout A (with pagination)
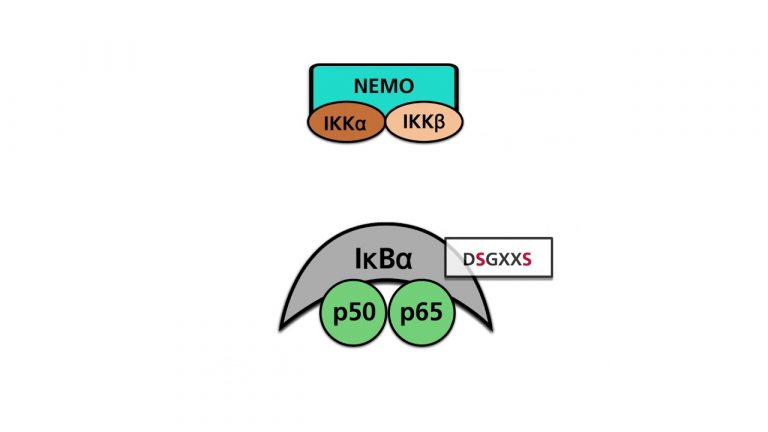
NF-κB transcription factors can be activated by different pathways. The canonical NF-κB pathway starts with the activation of the TNFα receptor. The activated receptor recruits several intracellular proteins that pass the signal on to a multiprotein complex made up of NF-κB and other...
The alternative NF-κB pathway is activated by several ligands such as CD40L or lymphotoxin β and their receptors. The activated receptor lifts the blockage of the proteolytic degradation of p100, a protein of the NF-κB protein family. Partial degradation leads to the protein p52, which...
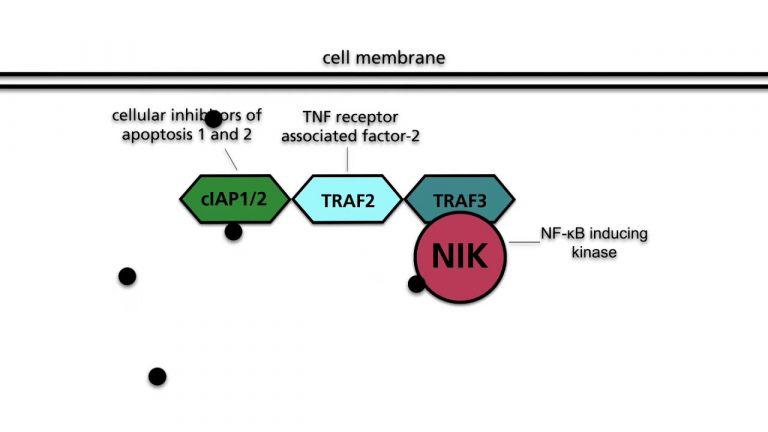
The NF-kB pathway is constitutively active in multiple myeloma and other human tumors. The activation is based mainly on mechanisms that lead to an increased level or to the activation of the NF-kB inducing kinase (NIK). Mechanisms include the deletion of genes encoding proteins that...
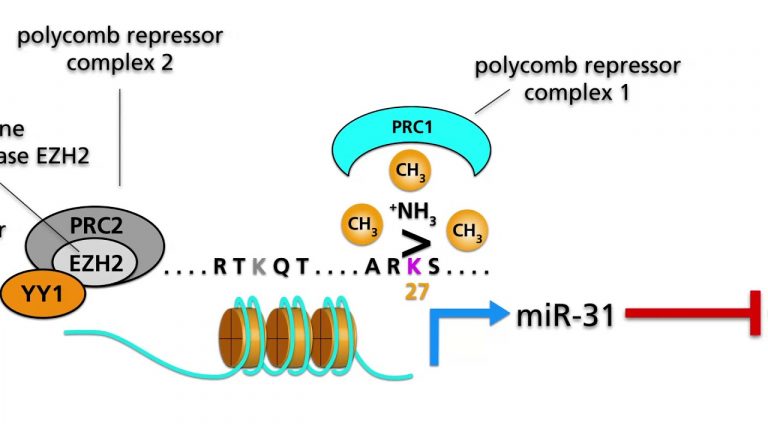
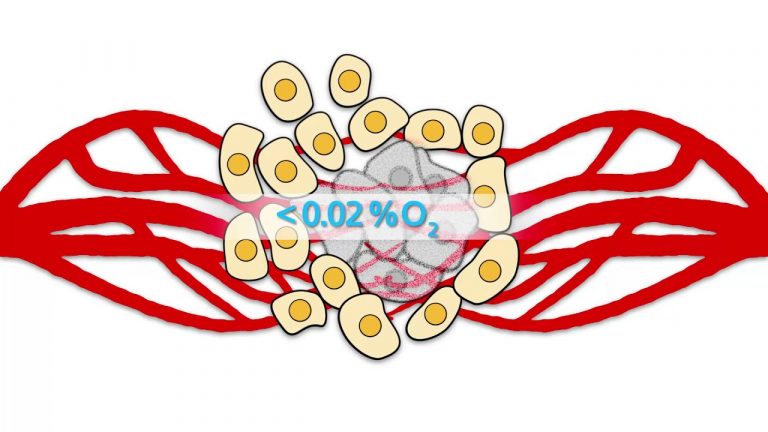
Cells within growing tissues need a constant supply of oxygen. Under physiological conditions, the delivery of oxygen is well regulated; under pathological conditions, however, the availability of oxygen may be limited. For example, severe hypoxia may develop in rapidly growing tumors. In...